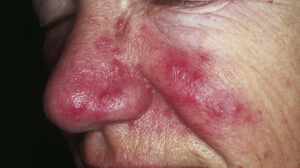
Chronic idiopathic urticaria: The causes, symptoms, treatment, and how to care of it – Urticaria (also known as “‘hives, itching, or Chilblains”) is the condition of the skin disorder be vascular reaction against an assortment of reasons, usually caused by an allergic reaction, which which has the characteristics of reddish skin (erythema) with slight edema or prominent (elevated) skin bounded which arises quickly after triggered by precipitation factors and disappears slowly.
A wide range of variants of urticaria include acute immunoglobulin E (IgE) – mediated urticaria, chemical-induced urticaria (non-IgE-mediated), urticaria vasculitis, autoimmune urticaria, cholinergic urticaria, cold urticaria, mastocytosis, Muckle-Wells syndrome, and many others.
The causes of Chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Although generally the cause of urticaria is known because of reaction allergic to certain allergens, but in other conditions where unknown cause significantly, then known the term idiopathic urticaria. Erythema and edema firmly unbounded involving the dermis and epidermis that is very itchy. Urticaria can be acute (lasting less than 6 weeks) or chronic (over 6 weeks).
Here are triggers of chronic urticaria:
- In some cases, chronic urticaria is part of food allergies. For example, beans, fish, wheat, eggs, or dairy products and their derivatives.
- In other cases, allergies, dust mites, pollen or flowers could also contribute to the onset of urticaria.
- In some people, insect bites can also trigger the onset of urticaria.
Unfortunately, up to now, this skin condition has often attacked many people is not yet known for sure cause. In addition to allergies in general, experts believe that utricaria could be caused by an autoimmune disease.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy cells that exist in the body itself. Your immune system even consider that your cells are foreign organisms that are dangerous.
Symptoms of Chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Urticaria is generally marked by a reddish rash on the skin, which stands out and can be palpated, where its form can resemble a circular or straight line. This can occur in all parts of the body. This unnatural redness in the body can be recognized easily. Generally, sufferers also find out the cause of the redness factor.
Here are some signs and symptoms that accompany this disease:
- A great itching is a subjective complaint that is always present in sufferers. These complaints can also be sensations such as burning or impaled.
- Description of redness on the skin are generally unbounded firmly, accompanied by the appearance of puffiness or middle part of the skin will also look more pale. This should be distinguished from insect bites or exposure to ultraviolet rays.
- If the skin disorder involving the deeper parts, then it will look swollen with boundaries that are not assertive. This is referred to as angioedema, which often manifests on the eyelids and lips.
- This disease can also occur due to pressure from clothing, such as around the waist and its shape in accordance with pressure into the cause.
The possibility of risks will arise.
Sufferers of chronic Urticaria have risk to experience abnormalities in the immune system:
- Lupus.
- Thyroid disease.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Type 1 diabetes.
- Sjogren’s Syndrome.
But with proper handling will be able to control the complaints that you are experiencing.
Treatment of Chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Handling of chronic Urticaria include:
- Handling the main causes of urticaria.
- The giving of antihistamine drugs (for example Loratadine, Cetirizine, and more).
- If the complaint is not resolved it can be given the drug such as corticosteroids, antidepressants, etc.
If your itchiness is not resolved, it is advisable to consult a doctor again. The doctor will perform a physical examination to analyze the improvements experienced and complaints that have not been resolved, then determine the appropriate therapy with your current condition.
How To Care For Chronic idiopathic urticaria.
While you wait for the itching and swelling disappear, here are some tips on caring for chronic idiopathic urticaria:
- Avoid hot water, use warm water instead.
- Use a mild soap.
- Apply cold compresses or wet cloth to the affected skin area.
- Try to work and sleep in a cool room.
- Use a thin and loose clothing.
Thank you very much for reading Chronic idiopathic urticaria: The causes, symptoms, treatment, and how to care of it.